Ubertooth One: A Bluetooth Network Hacking Tool
Ubertooth One: A Bluetooth Network Hacking Tool
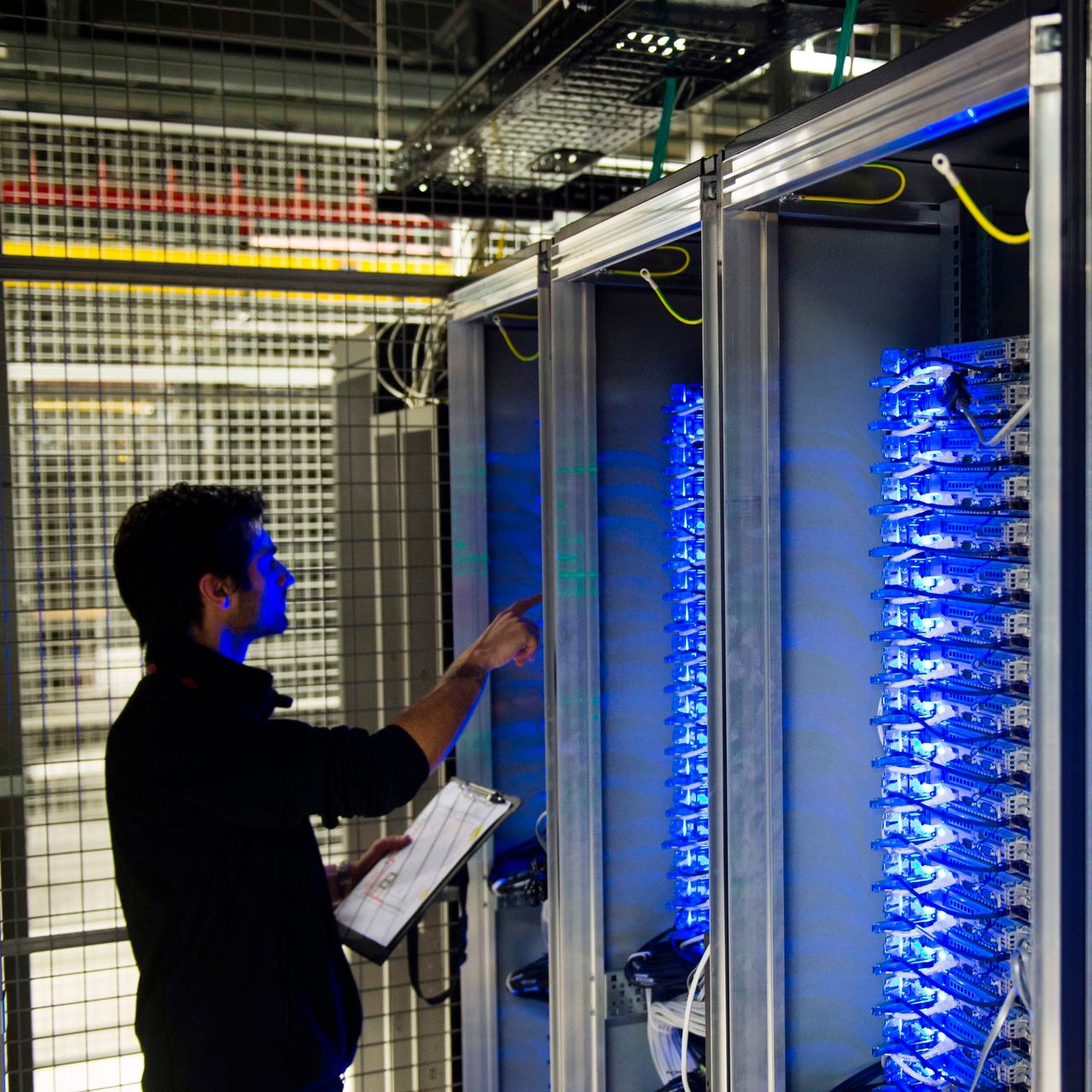
bertooth One is a cheap, open-source Bluetooth network sniffer. Unlike Wi-Fi, which has had a wide range of free network monitoring tools for years, Bluetooth has remained pretty closed. Michael Ossman is about to change this, with his Ubertooth Kickstarter project.
The Ubertooth One is a USB plug with an antenna, and a ARM Cortex-M3 processor-based board in-between. Plug it into your computer and you can use it with various wireless monitoring tools like Kismet. The Ubertooth allows you to use Bluetooth in monitoring mode. This "promiscuous" mode makes the radio pass everything that it picks up onto the host computer. Normally, wireless receivers will ignore anything not addressed to them. In promiscuous mode, you can sniff and gather data meant for other devices.
These tools can be used for testing network security, or for hacking. Kismet, for example (and derivatives like the Mac OS X version KisMac) can be used to crack Wi-Fi networks' passwords.
Until now, Bluetooth monitoring hardware would cost upward of $1,000. Ossman's device will cost just $100 and, because both the software and hardware are open-source, you can build your own.
There are three major components of Project Ubertooth:
hardware: The hardware design of Ubertooth One is quite stable.
firmware: This is software that executes on the ARM processor on the Ubertooth One itself. This page assumes that you have the USB bootloader plus bluetooth_rxtx firmware installed on your board (which is typically what is installed at the time of assembly). The bluetooth_rxtx firmware is moderately stable but is likely to be enhanced as time goes on.
host code: This is software running on a general purpose computer connected to the Ubertooth One via USB. The sample host code for Project Ubertooth is in active development and will likely change a great deal in the coming months.
Ubertooth One is a development platform. The true power of the device is best realized when you start writing your own software and adapting it to your needs. If you are just getting to know the board, however, it can be helpful to try out open source code that others have made available. This guide will help you get started with your Ubertooth One by introducing you to some useful host code from the Ubertooth software repository.
LAP SNIFFING
Bluetooth packets start with a code that is based on the Lower Address Part (LAP) of a particular Bluetooth Device Address (BD_ADDR). The BD_ADDR is a 48 bit MAC address, just like the MAC address of an Ethernet device. The LAP consists of the lower 24 bits of the BD_ADDR and is the only part of the address that is transmitted with every packet.
The most important passive Bluetooth monitoring function is simply capturing the LAP from each packet transmitted on a channel. LAP sniffing allows you to identify Bluetooth devices operating in your vicinity.
In order to sniff LAPs, you'll have to compile the tools in host/bluetooth_rxtx. These are command line programs intended to work with the bluetooth_rxtx firmware installed on your Ubertooth One. Follow the instructions in the README file in that directory to install the the prerequisite libbtbb, a library for Bluetooth baseband functions. You can install libbtbb from a file release rather than git if you prefer.
Once libbtbb is installed, just type "make" in the host/bluetooth_rxtx directory to compile the tools there. Then make sure your Ubertooth One is plugged in and execute:
$ ./ubertooth-lap
You should see various random LAPs detected. Due to uncertainties in identifying Bluetooth packets without prior knowledge of an address, it is normal for this process to identify false positives at a rate of roughly 20 per minute. When you see the same LAP detected more than once, that is very likely an actual Bluetooth transmission.
Generate some Bluetooth traffic and enjoy the show. I like to use a mobile phone or other Bluetooth device to perform an inquiry (usually called "find new Bluetooth devices" or something similar) to make sure that everything is working properly. An inquiry should produce lots of packets with the LAP 0x9e8b33.
KISMET
More advanced Bluetooth sniffing has been implemented in the form of a plugin for Kismet, the venerable 802.11 monitoring tool. In order to compile the Kismet-Ubertooth plugin, you will need a Kismet source tree matching the installed version. The easiest way to make this work is to uninstall any binary Kismet installation you may have installed and then download the Kismet source and follow the instructions to compile and install from the fresh source code. Once Kismet is installed, follow the instructions in host/kismet/plugin-ubertooth/README to install and use the plugin.
Notice that Kismet-Ubertooth identifies not only the LAP but also the 8 bit Upper Address Part (UAP) of detected devices as it is able. This is done by analyzing the timing and other characteristics of multiple packets over time. Another advantage of Kismet is that it dumps complete decoded packets to a pcapbtbb file that can be read with a Wireshark plugin that is distributed with libbtbb. Full packet decoding is only possible when the packet's UAP has been determined.